Read on to discover
- Causes of impacted wisdom teeth
- Symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth
- Diagnosis of impacted wisdom teeth
- Treatment options for impacted wisdom teeth
- Prevention strategies for impacted wisdom teeth
Dr Nick White has a keen interest in preventative dental care, oral surgery, children’s dentistry and treating gum disease. He visits the St. Stephens Hospital to provide dental treatment under general anaesthetic.
Key takeaways
- Impacted wisdom teeth occur where there is insufficient space for the wisdom teeth to move into the mouth properly.
- You should consult a dentist if you suspect you have symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth.
- If you have trouble with your wisdom teeth, your trusted dentist can provide prompt intervention.
What are wisdom teeth?
Wisdom teeth are the third and last set of molars that usually appear during late adolescence or early adulthood. Most people have four wisdom teeth, but sometimes more or fewer develop. Some people’s wisdom teeth don’t grow at all.
Sometimes, wisdom teeth come through the gums without problems and function like any other teeth. They are a little more difficult to keep clean, being so far back in the mouth. But with good home care and regular dental check-ups, the third molars may be a trouble-free addition to a person’s set of teeth.
However, wisdom teeth are sometimes troublesome, which I’ll describe in this article.
What does “impacted wisdom teeth” mean?
Impacted wisdom teeth refer to a condition where there isn’t enough space for third molars to emerge properly through the gums and into alignment with the rest of the teeth. When wisdom teeth remain trapped under the gum, either partially or fully, they’re considered to be impacted.
Causes of impacted wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth can become impacted for a variety of reasons. In most cases, there is simply not enough room in the mouth for them to emerge properly through the gums.
The growth pattern of wisdom teeth can also lead to impaction. For example, if the wisdom teeth grow at an angle instead of straight up, they may become trapped under the gum line.
Regardless of the cause, if you suspect impacted wisdom teeth, you should seek professional advice to prevent further complications.
Identifying symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth
Some of the most common symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Difficulty opening the jaw or jaw stiffness
- Bleeding or swollen gums at the back of the mouth
- Trouble chewing food
- Bad breath, unpleasant tastes, or noticeable food traps towards the back of the mouth.
I always encourage people to take action on any such warning signs and make an appointment with their dentist as soon as possible. Even if impacted wisdom teeth aren’t the cause of these symptoms, a dentist can identify the source.
Sometimes, impacted wisdom teeth cause no noticeable discomfort or issues (dentists refer to these as ‘asymptomatic’). Unfortunately, this lack of symptoms doesn’t always mean the wisdom teeth are okay. So if an x-ray has confirmed the presence of wisdom teeth under the gums in a young person, I’ll repeat the x-ray periodically to ensure nothing untoward is happening.
Oral health risks associated with impacted wisdom teeth
Untreated, impacted wisdom teeth can lead to various oral health risks. The most common include
Infection
One of the most common issues is the risk of infection, which can occur if bacteria become trapped under the gum line around the impacted tooth.
Tooth decay and gum disease
It’s difficult (and sometimes impossible!) to properly clean a wisdom tooth that has only partly emerged through the gum.
If plaque builds up around an impacted wisdom tooth or the space becomes a food trap, decay may develop in the wisdom tooth and/or the adjacent second molar.
The presence of plaque bacteria can also lead to gum disease.
Damage to neighbouring teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth can also cause damage to the neighbouring teeth through a process called resorption. The presence of the wisdom tooth can cause a “resorption cavity” in the second molar’s crown or root. This condition can cause the loss of the second molar.
Cysts and tumours
Occasionally, a cyst or tumour can develop around an impacted wisdom tooth. Cysts can cause damage to the nearby roots and the jawbone supporting the teeth. Tumours may be benign or malignant. Cysts and tumours are usually removed along with the wisdom tooth and other involved teeth.
Diagnosing impacted wisdom teeth
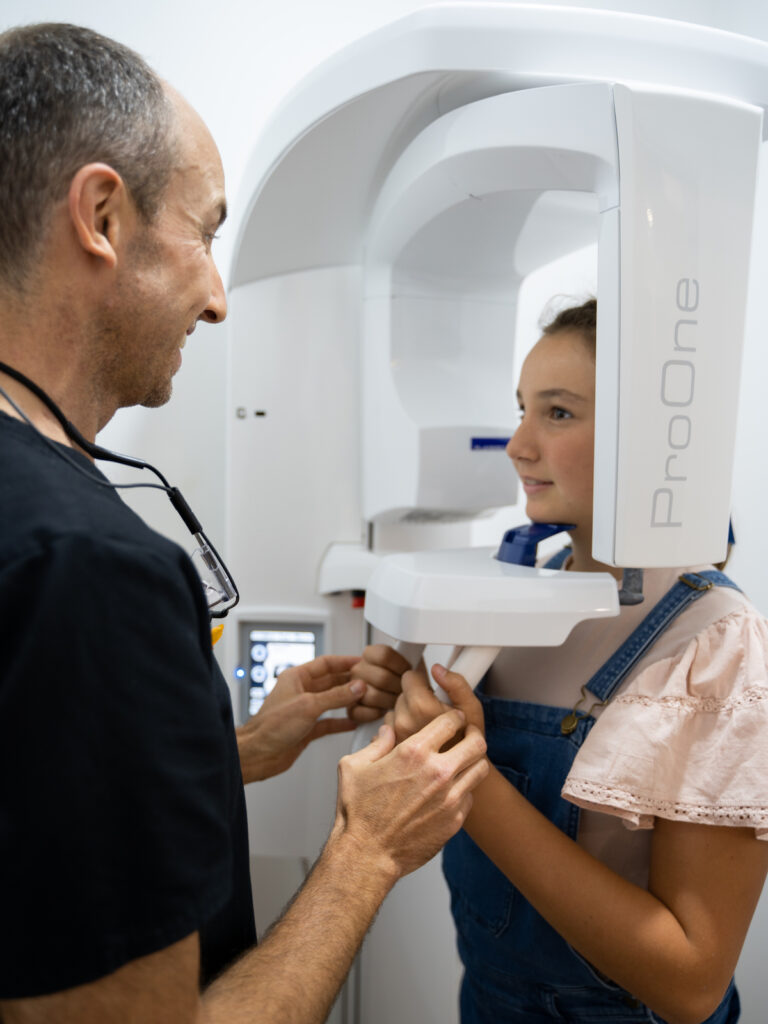
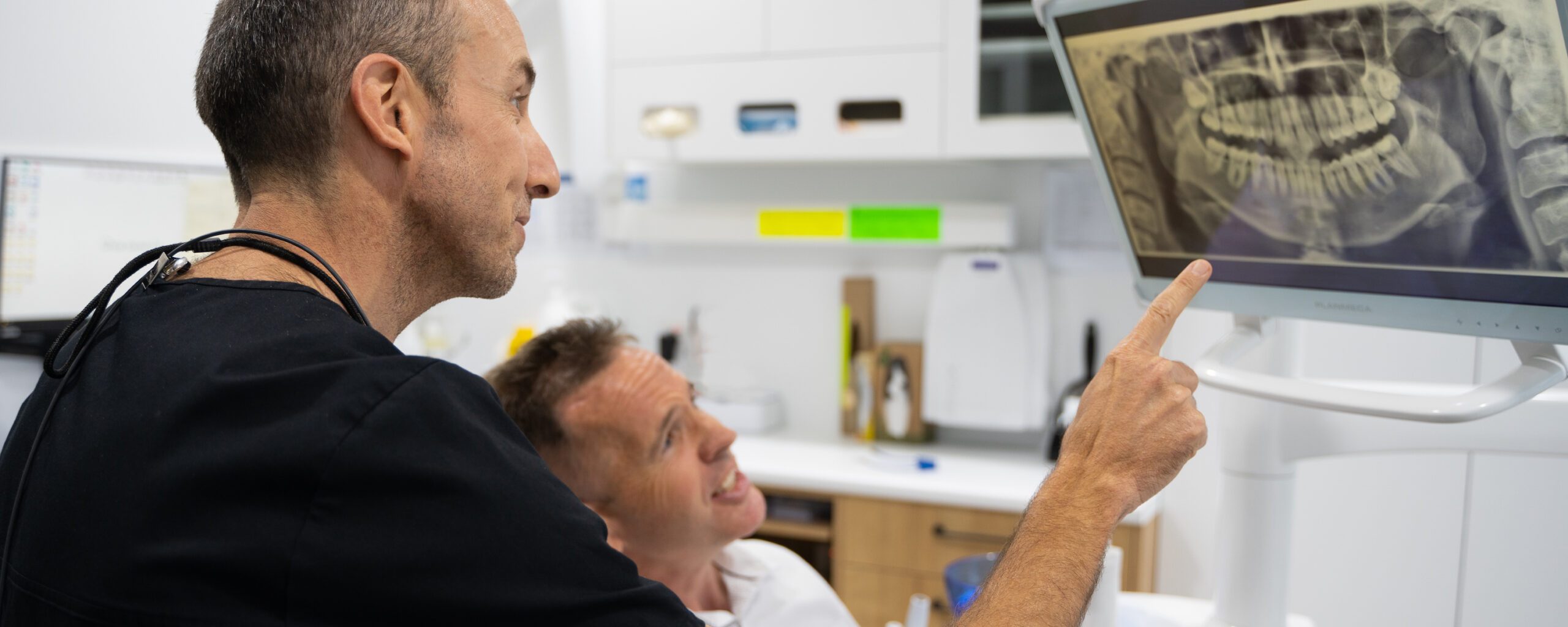
Dentists use a variety of imaging techniques to diagnose impacted wisdom teeth. X-rays and CT scans are commonly employed to provide a clear picture of the position and condition of the wisdom teeth within the jaw.
These imaging techniques help dentists
- accurately assess the severity of impaction and
- determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each case.
The most frequently used X-ray for screening for the presence of wisdom teeth is called an orthopantomogram or OPG. An OPG is a large panoramic image of the jaws that provides a lot of information about the teeth and bone structure of the upper and lower jaws.
In 2021, we installed an OPG machine in our rooms at White Dental Co. Its presence means our patients don’t have to go elsewhere to get their OPGs taken. Within minutes, we can take an OPG image and identify
- whether wisdom teeth are present
- whether wisdom teeth are impacted or likely to become impacted
- clues about the health of the wisdom teeth and their neighbours
- information to assist in extracting wisdom teeth, should this treatment be necessary.
Treatment options for impacted wisdom teeth
Depending on the severity of impaction, treatment options for impacted wisdom teeth may include
- monitoring and observation
- extraction, which may be surgical or non-surgical.
Monitoring and observation
In some cases, impacted wisdom teeth may not require immediate intervention. If the impacted teeth are not causing immediate issues or discomfort, your dentist may suggest monitoring them via regular checkups.
Extraction of impacted wisdom teeth
I will generally recommend the removal of wisdom teeth if
- They are causing ongoing and frequent pain or infections
- They have or are likely to cause damage to the neighbouring teeth
- An orthodontist has requested their removal as part of an orthodontic treatment plan.
If wisdom teeth are partly or fully encased in the jawbone, surgical removal will be necessary. This procedure involves an incision of the gums and, sometimes, removal of some bone to provide better access to the tooth. Following the procedure, the gum is stitched back into place. The patient will be given instructions on how to care for the extraction site while it’s healing.
Non-surgical extraction may be possible for less severe cases of impaction.
Extraction of impacted wisdom teeth should only be performed by a qualified dentist or oral surgeon with experience in this procedure. As with any surgery, there are risks associated with the removal of wisdom teeth. Your dentist will explain these to you and obtain your informed consent before proceeding with treatment.
Options for anaesthesia during wisdom tooth extractions
Anaesthesia options during wisdom tooth extraction depend on the patient’s preference and the complexity of the procedure.
Local anaesthesia is commonly used in our rooms for less complex wisdom tooth extractions. This involves numbing the area around the tooth, allowing the patient to remain awake and alert during the procedure.
Conversely, general anaesthesia renders the patient unconscious and is typically reserved for more complex extractions or patients with high levels of anxiety. If a patient requests a general anaesthetic, we book an operating theatre at nearby St Stephen’s Hospital for a day-stay procedure.


Your dentist or oral surgeon will discuss the anaesthesia options with you and help determine the most appropriate choice for your situation. Adhering to pre-surgery instructions, including food and drink restrictions before the procedure, is crucial for a safe and successful extraction.
Post-extraction care and recovery
Following the removal of wisdom teeth, I encourage my patients to
- focus on their recovery by taking plenty of rest for the first few days after the procedure
- pay careful attention to their post-procedure wound care to minimise potential complications.
To manage pain and swelling, patients can:
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers as instructed by their dentist
- Apply ice packs to the face
- Gently rinse their mouth with a saltwater or antiseptic mouthwash solution 24 hours after the surgery.
I tell my patients to avoid vigorous rinsing in the first couple of days, as this can disrupt the formation of blood clots in the empty socket and potentially lead to a dry socket.
You should follow your dentist’s post-extraction care instructions to manage pain and swelling. These instructions may include
- avoiding certain foods
- refraining from smoking or using straws
- keeping the extraction site clean by brushing and flossing gently around the area.
Potential complications following wisdom teeth removal
Although serious complications following wisdom teeth removal are rare, it’s essential to know the potential risks and how to manage them.
When a patient’s wisdom teeth need to be removed, I’ll sit with them to explain the procedure and the potential risks. The general information I’ve included below may not apply to every case.
Dry socket
A dry socket is a condition that occurs when the blood clot that forms after surgery is dislodged from the socket, exposing the underlying bone. A dry socket is characterised by constant, throbbing pain lasting several days.
Nerve damage
There is a risk of nerve damage when the impacted wisdom tooth sits close to a major nerve. Because of this proximity, the nerve may be bruised or damaged during tooth removal. Nerve damage can lead to temporary or permanent numbness of the teeth, gums, lips, chin, cheeks, or tongue.
If the major nerve to the tongue is damaged, the sense of taste may be altered.
Infection
Infection can occur if bacteria enter the extraction site.

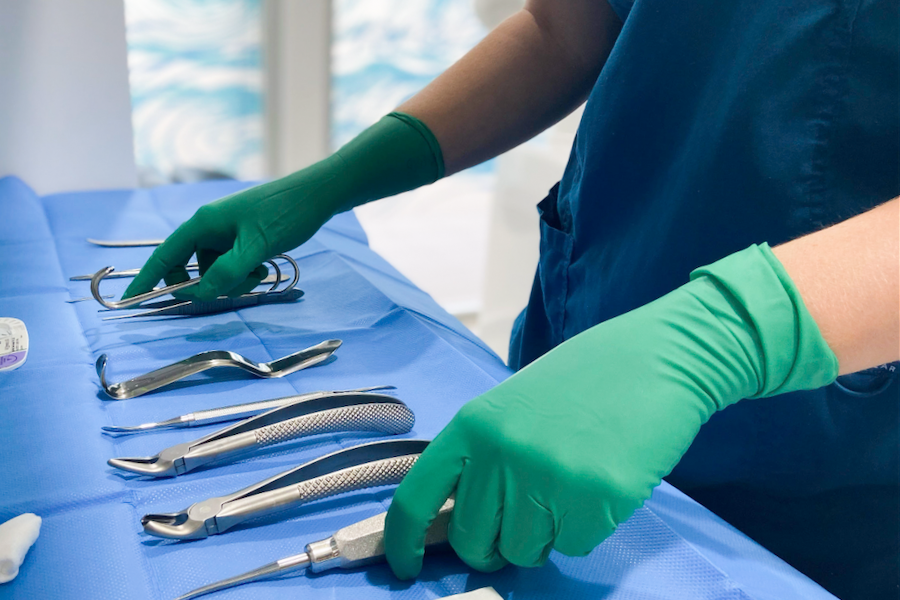
We minimise the likelihood of infections by ensuring our instruments and materials are clean and sterile.
The patient can minimise the likelihood of infection by carefully following their dentist’s post-operative care instructions.
After wisdom tooth extraction, seeking professional advice for any unusual symptoms or concerns is imperative.
Preventing problems associated with impacted wisdom teeth.
The best way to prevent problems associated with impacted wisdom teeth is to monitor their growth and development and address potential concerns before they escalate. You can do this by having
- regular dental check-ups
- a screening x-ray to find out whether wisdom teeth are present
- periodic follow-up x-rays to monitor the health of unerupted wisdom teeth
It’s also important to keep all your teeth and gums clean with twice-daily brushing and daily flossing.
Conclusion
Impacted wisdom teeth can be caused by a lack of space, obstruction, or abnormal position and may lead to symptoms such as pain. Awareness of impacted wisdom teeth is essential to avoid potential complications and ensure optimal oral health.
You should always consult your trusted dentist for professional advice and treatment for impacted wisdom teeth. Your dentist can help mitigate the risks associated with impacted wisdom teeth, paving the way for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
If you don’t have a regular dentist and are concerned about your wisdom teeth, give White Dental Co. a call. We’ll take great care of you and your ongoing dental health.
Additional resources
For further information on wisdom teeth, consult the following resources:



